Climate Change Adaptation Strategies for a Resilient Future
Climate Change Adaptation Strategies are crucial as the world faces unprecedented environmental challenges. These strategies encompass a range of approaches designed to help communities and ecosystems adjust to the inevitable impacts of climate change. From rising sea levels to extreme weather events, understanding and implementing effective adaptation measures is essential for safeguarding our future.
Climate change is not just an environmental issue; it influences economic stability, public health, and social equity. By exploring the various types of adaptation strategies, their significance across different sectors, and the involvement of communities and technologies, we can better prepare for the future. This overview sets the stage for a deeper understanding of how we can effectively confront the realities of a changing climate.
Overview of Climate Change Adaptation
Climate change adaptation refers to the process of adjusting to current or expected changes in the climate. This includes alterations in practices, processes, and structures to mitigate damage or exploit beneficial opportunities. As climate change poses significant risks to human health, agriculture, water supply, and biodiversity, effective adaptation strategies become essential for reducing vulnerability and enhancing resilience.Adaptation strategies are vital in addressing the multifaceted impacts of climate change.
They not only aim to protect people and ecosystems from the adverse effects but also enhance the capacity of communities and economies to thrive in altered environmental conditions. As climate-related hazards such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels become more frequent, the adoption of robust adaptation measures is critical for ensuring sustainability and safeguarding the well-being of populations.
Key Sectors Affected by Climate Change
Various sectors are profoundly affected by climate change, each requiring tailored adaptation strategies to address their unique vulnerabilities. Understanding these sectors and their specific adaptation needs is crucial for effective climate change response. The following are key sectors and the adaptation strategies associated with them:
- Agriculture: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to crop failures and reduced yields. Adaptation strategies may include developing climate-resilient crops, implementing water-saving technologies, and diversifying farming practices to sustain food production.
- Water Resources: Altered rainfall patterns and increased evaporation rates can strain water supplies. Effective adaptation could involve investing in efficient irrigation systems, constructing water storage facilities, and protecting watersheds to preserve water quality.
- Health: Climate change can exacerbate health issues, leading to increased heat-related illnesses and the spread of vector-borne diseases. Adaptation efforts in this sector may encompass improving healthcare infrastructure, enhancing early warning systems for disease outbreaks, and promoting public health education.
- Coastal Areas: Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities and ecosystems. Adaptation measures include constructing sea walls, restoring mangroves and wetlands, and implementing managed retreat strategies for vulnerable populations.
- Forestry: Climate change can alter forest health and biodiversity. Strategies for adaptation may involve sustainable forest management, reforestation projects, and the promotion of species resilient to changing climates.
“Adaptation is not a luxury but a necessity in a world increasingly shaped by climate change.”
Types of Adaptation Strategies
Adaptation strategies for climate change are essential for communities to minimize risks and enhance resilience against the impacts of a changing climate. These strategies can vary significantly based on geographical contexts, socio-economic conditions, and existing infrastructures. Understanding the different types of adaptation strategies is crucial for developing effective measures tailored to specific needs.Adaptation strategies can generally be categorized into three main types: infrastructural, ecological, and social.
Each of these strategies plays a significant role in addressing climate-related challenges, ensuring that communities are well-prepared to cope with the impacts of climate change.
Infrastructural Adaptation Strategies
Infrastructural adaptation strategies involve the modification or enhancement of physical structures to withstand climate impacts. This type of adaptation is particularly important in urban areas prone to flooding, extreme heat, or sea-level rise.
- Flood defenses: Cities like New York have invested in advanced flood barriers and levees to protect against storm surges, especially after Hurricane Sandy in 2012.
- Green roofs: Implemented in cities such as Chicago, green roofs help mitigate urban heat and manage stormwater runoff, contributing to improved urban resilience.
- Stormwater management systems: Cities like Singapore have developed comprehensive drainage systems to manage heavy rainfall and prevent flooding, incorporating features like bio-swales and retention ponds.
Infrastructural strategies are vital in densely populated regions where climate impacts can be severe. They not only protect against imminent threats but also enhance the overall sustainability of urban environments.
Ecological Adaptation Strategies
Ecological adaptation strategies focus on preserving and restoring natural ecosystems to enhance their resilience to climate change. These strategies are essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services that communities rely on.
- Wetland restoration: Initiatives in Louisiana aim to restore coastal wetlands which act as natural buffers against storm surges and provide essential habitats for wildlife.
- Reforestation: Countries like Brazil promote reforestation programs in the Amazon rainforest to combat deforestation and enhance carbon sequestration while improving soil health.
- Agroforestry practices: In places like Kenya, integrating trees into agricultural lands helps improve soil quality, reduce erosion, and create microclimates that enhance crop resilience.
Ecological strategies are particularly important in rural areas and regions with rich biodiversity, as they not only protect the environment but also enhance local livelihoods dependent on these ecosystems.
Social Adaptation Strategies
Social adaptation strategies emphasize community engagement and education to foster resilience against climate change impacts. These strategies focus on enhancing social networks and capacity building.
- Community workshops: In the Philippines, community-driven workshops educate residents on disaster preparedness and response, building local capacity to deal with typhoons and floods.
- Policy advocacy: Organizations in Bangladesh work with local communities to advocate for policies that support climate adaptation, ensuring that the voices of vulnerable populations are heard.
- Insurance schemes: In countries like Ethiopia, innovative insurance products are developed to provide financial security to farmers facing climate-related crop failures, enabling them to recover more swiftly.
Social strategies play a crucial role in empowering communities, ensuring that they have the knowledge and resources needed to adapt effectively to climate change, particularly in marginalized groups most affected by climate impacts.
Policy Frameworks for Adaptation
Climate change adaptation requires a robust policy framework to ensure effective strategies are in place to address the challenges posed by a changing climate. This framework encompasses local, national, and international policies aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change while enhancing resilience in communities and ecosystems. Understanding these policies is crucial for identifying gaps and opportunities for further action.Governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play pivotal roles in promoting adaptation initiatives through policy development, implementation, and advocacy.
While governments establish legal and regulatory frameworks, NGOs often provide grassroots support, expertise, and funding for local adaptation projects. Collaborative efforts between these entities are essential for the success of adaptation strategies.
Existing Policies Supporting Climate Change Adaptation
Numerous policies exist across different levels of governance that specifically address climate change adaptation. These policies often include frameworks for disaster risk management, land use planning, and sustainable development. The table below summarizes key policies and their objectives related to adaptation.
| Policy | Objective |
|---|---|
| National Adaptation Programmes of Action (NAPA) | To identify priority activities that address the urgent and immediate needs of vulnerable countries in adapting to climate change. |
| Climate Adaptation Strategy (CAS) | To Artikel a comprehensive approach for managing climate risks while promoting sustainable development and community resilience. |
| European Union Adaptation Strategy | To foster climate resilience across EU member states by integrating climate adaptation into various policies and practices. |
| United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) | To promote international cooperation on climate change adaptation through mechanisms like the Green Climate Fund. |
“Effective adaptation policies are essential for safeguarding communities and natural systems from the adverse effects of climate change.”
The role of government bodies often includes creating legal frameworks that mandate adaptation planning, funding for research, and facilitating stakeholder engagement. Conversely, NGOs typically focus on raising awareness, mobilizing community involvement, and implementing on-the-ground projects that align with broader policy goals. Together, these actors contribute to building a more resilient society capable of facing climate uncertainties.
Community Engagement in Adaptation
Community involvement plays a crucial role in developing and implementing effective climate change adaptation strategies. When local populations are engaged, they bring invaluable insights into their unique challenges and opportunities, which can significantly enhance the relevance and efficiency of adaptation efforts. Engaging communities fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, making them more likely to support and sustain these initiatives over time.The involvement of communities in adaptation strategies can lead to innovative and practical solutions tailored to local conditions.
For instance, community-led initiatives often leverage local knowledge and resources, ensuring that solutions are not only environmentally sustainable but also socially acceptable. A notable example is the “Green Roofs for Healthy Cities” initiative in Toronto, where community members collaborated to create green spaces on rooftops, mitigating urban heat and improving biodiversity in the city.
Examples of Community-Led Initiatives
Community-led initiatives have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in addressing local climate challenges. These initiatives often stem from grassroots organizations or local governments working closely with residents. Some successful examples include:
- Community Forest Management: In Nepal, local communities have successfully managed forest resources, leading to reforestation and increased biodiversity while simultaneously addressing soil erosion and water management.
- Flood Resilience Programs: The “Living Shorelines” project in Virginia focuses on community engagement to restore coastal ecosystems, reducing vulnerability to flooding and erosion.
- Urban Agriculture Initiatives: In Detroit, community gardens are transforming vacant lots into productive green spaces, improving food security and community resilience against climate impacts.
Best practices for engaging communities in adaptation efforts can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these strategies. These practices ensure that initiatives are inclusive, participatory, and reflective of the community’s needs and capabilities.
Best Practices for Engaging Communities
Effective community engagement in climate change adaptation involves several key practices, which can lead to more sustainable and impactful outcomes:
- Building Trust: Establishing trust through transparent communication and consistent interaction with community members is essential for fostering collaboration.
- Incorporating Local Knowledge: Utilizing local expertise and traditional practices can create more relevant and effective adaptation strategies.
- Facilitating Capacity Building: Providing training and resources empowers communities to actively participate in adaptation efforts and manage their own resources sustainably.
- Creating Inclusive Platforms: Ensuring diverse representation in decision-making processes includes marginalized groups, enhancing the effectiveness and equity of adaptation strategies.
- Monitoring and Feedback: Implementing mechanisms for ongoing evaluation and feedback allows communities to adapt strategies based on real-time challenges and successes.
Community engagement is pivotal for successful climate change adaptation. By fostering local involvement and leveraging community-driven initiatives, we can develop more effective strategies that address the unique challenges faced by communities.
Technological Innovations for Adaptation
Technological advancements play a critical role in enhancing our ability to adapt to the effects of climate change. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns become more unpredictable, innovative technologies provide tools that help communities manage risks, improve resilience, and ensure sustainable development. This segment delves into various technological innovations that support climate change adaptation, showcasing their benefits, applications, and associated risks.
Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems utilize advanced technology to monitor and predict climate-related hazards, providing timely alerts that can save lives and protect property. These systems leverage data from satellites, meteorological stations, and ocean buoys to offer real-time information about extreme weather events.
Importance of Early Warning Systems
These systems help communities prepare for disasters such as floods, hurricanes, and heatwaves, allowing for timely evacuations and resource allocation.
Case Study
In Bangladesh, the introduction of a comprehensive early warning system for cyclones has significantly reduced fatalities. By disseminating alerts through mobile phones and community radios, the government has empowered citizens to take proactive measures.
Technological Components
Satellite imagery for monitoring weather patterns.
Mobile applications for real-time notifications.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for mapping risk areas.
Climate-Resilient Crops
The development of climate-resilient crops is a major breakthrough in agricultural adaptation to climate change. These crops are engineered to withstand extreme weather conditions, pests, and diseases, ensuring food security in changing climates.
Benefits of Climate-Resilient Crops
These innovations enhance yield stability, reduce dependency on chemical fertilizers, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Case Study
In sub-Saharan Africa, the introduction of drought-resistant maize varieties has helped farmers cope with erratic rainfall patterns. These crops have shown to increase yields by up to 30% in drought-prone areas, contributing to food security and economic stability.
Technological Methods
Genetic modification to enhance resilience traits.
Breeding programs focusing on traditional and wild crop varieties.
Precision agriculture techniques to optimize resource use.
Smart Water Management Technologies
Water scarcity is a pressing issue exacerbated by climate change, making smart water management technologies essential for adaptation. These technologies enable efficient water usage and conservation.
Overview of Smart Water Technologies
Technologies such as sensors, automated irrigation systems, and water recycling methods help optimize water distribution and usage.
Case Study
In Israel, advanced irrigation systems utilize drip technology, which significantly reduces water waste while increasing agricultural productivity. This method has transformed arid regions into productive farmland, showcasing a sustainable approach to water management.
Key Innovations
Soil moisture sensors for precise irrigation.
Rainwater harvesting systems to increase water availability.
Desalination plants for converting seawater into freshwater.
Risks Associated with Technological Reliance, Climate Change Adaptation Strategies
While technological innovations offer numerous advantages for climate change adaptation, they also come with certain risks that need to be carefully considered.
Potential Risks
Over-reliance on technology can create vulnerabilities, such as technological failures, high costs, and potential inequities in access.
Example of Risk
In regions where early warning systems are not uniformly implemented, marginalized communities may remain uninformed and unprotected during crises, highlighting the importance of equitable technology deployment.
Balancing Technology Use
It is crucial to integrate traditional knowledge and community involvement with technological solutions to enhance resilience and ensure that all community members can benefit from adaptation efforts.
Economic Considerations in Adaptation
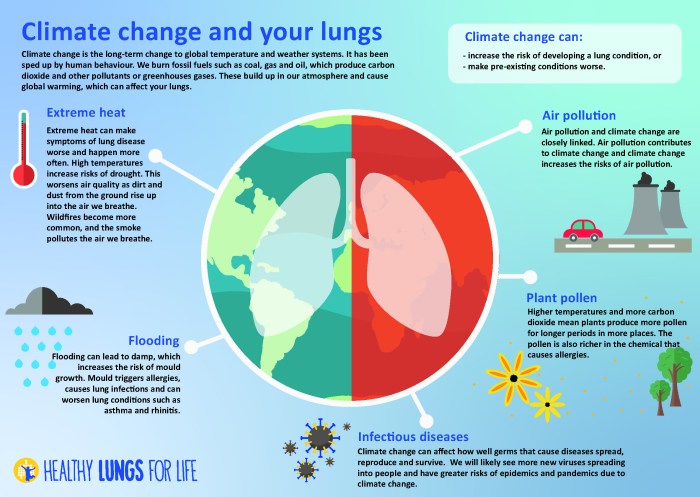
Source: europeanlung.org
The economic aspects of climate change adaptation are critical in understanding the viability and effectiveness of various strategies. As the impacts of climate change become increasingly evident, analyzing the financial implications of adaptation strategies allows policymakers, businesses, and communities to make informed decisions that mitigate risks while promoting sustainability. Economic considerations also reflect the balance between immediate costs and long-term savings that can be achieved through proactive measures.The economic impacts of climate change are vast, affecting a range of sectors including agriculture, infrastructure, and health.
As climate-related events become more frequent, the costs associated with damage and recovery rise significantly. For instance, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reported that the U.S. experienced over $99 billion in weather and climate disasters in 2020 alone. Investing in adaptation strategies can reduce these costs by enhancing resilience and mitigating potential losses.
Cost-Effectiveness of Adaptation Strategies
Understanding the cost-effectiveness of adaptation strategies is essential for allocating resources efficiently. Investment in adaptation often results in substantial long-term savings by avoiding damages, enhancing productivity, and ensuring the sustainability of essential services. A comprehensive analysis reveals that for every dollar spent on adaptation, communities can save several dollars in future disaster recovery costs.The following table Artikels various adaptation strategies, their investment needs, and potential long-term savings:
| Adaptation Strategy | Investment Needs (in millions) | Potential Savings (in millions) |
|---|---|---|
| Flood Defense Systems | 100 | 500 |
| Coastal Restoration | 75 | 300 |
| Water Conservation Initiatives | 50 | 200 |
| Urban Heat Mitigation | 60 | 150 |
This table illustrates that while initial investments may seem significant, the potential long-term savings highlight the financial prudence of investing in climate resilience. Analyzing these figures reveals that adaptation strategies not only protect communities but also serve as economically sound investments, reinforcing the argument for prioritizing climate change adaptation in policy frameworks.
“Investing in climate adaptation strategies can yield a return of 4 to 1 in savings on disaster recovery and infrastructure resilience.”
Monitoring and Evaluation of Adaptation Strategies: Climate Change Adaptation Strategies

Source: ftcdn.net
Monitoring and evaluation (M&E) are critical components in the implementation of climate change adaptation strategies. These processes help to assess the effectiveness of various adaptation efforts and ensure that they are meeting their intended goals. By establishing a robust M&E framework, stakeholders can make data-driven decisions, which ultimately leads to improved resilience and sustainability in the face of climate change.Effective monitoring of adaptation strategies involves a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods that track progress over time.
These methods can include remote sensing, surveys, and community feedback mechanisms. Remote sensing technologies can provide valuable data on environmental changes, while surveys can gauge community perceptions and adaptations. Furthermore, regular reviews and assessments are essential to evaluate whether the strategies are yielding the expected outcomes.
Indicators for Evaluating Success
Establishing indicators is fundamental for evaluating the success of adaptation strategies. Indicators serve as measurable signs of progress or impact, enabling stakeholders to assess whether adaptation efforts are effective. Key indicators can include:
- Reduction in vulnerability: Measured through metrics like decreased flooding incidents or improved water quality.
- Increased resilience: Assessed by the ability of communities to bounce back from climate-related shocks, such as droughts or extreme weather events.
- Community participation rates: Tracking the number of community members engaged in adaptation activities or decision-making processes.
- Economic stability: Evaluating changes in local economies, such as increased agricultural yields or job creation in green sectors.
These indicators allow for a comprehensive assessment of the adaptation strategies, as they encompass environmental, social, and economic dimensions.
Importance of Adaptive Management
Adaptive management is crucial in refining adaptation strategies based on the results obtained from monitoring and evaluation activities. This approach emphasizes learning and flexibility, enabling stakeholders to adjust their strategies in response to what the monitoring data reveal.Adaptive management involves:
- Feedback loops: Creating systems that allow for continuous learning from both successes and failures in adaptation efforts.
- Stakeholder involvement: Ensuring that all relevant parties, including local communities, are engaged in the review and adjustment processes.
- Iterative decision-making: Making informed adjustments to strategies based on evidence collected, ensuring that approaches remain relevant to changing climate conditions.
The significance of adaptive management cannot be overstated; it fosters resilience and responsiveness, enabling communities to thrive even amid the uncertainties posed by climate change.
“Monitoring and evaluation provide the roadmap for adaptive management, guiding stakeholders toward effective climate resilience strategies.”
Future Trends in Climate Change Adaptation
Source: scitechdaily.com
As we look to the future, the landscape of climate change adaptation is poised to evolve significantly, driven by advancements in climate science, shifting policies, and changing societal dynamics. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for effective planning and action. The next decade will likely witness a more integrated approach to adaptation, where technology, community engagement, and innovative policies converge to create resilient systems.
Emerging Trends in Adaptation Strategies
New findings in climate science are influencing the development of innovative adaptation strategies. For instance, advancements in predictive analytics enable more precise forecasting of climate impacts, allowing communities to implement proactive measures. This shift from reactive to proactive adaptation is essential for enhancing resilience.The integration of nature-based solutions (NbS) is a growing trend. NbS leverage natural processes to address climate challenges.
Examples include restoring wetlands to mitigate flooding and enhance biodiversity. These solutions not only reduce vulnerability but also provide co-benefits such as improved air quality and enhanced recreational spaces.
Influence of Policy Shifts on Adaptation Efforts
Policy frameworks are evolving to support more comprehensive adaptation strategies. Governments are increasingly recognizing the need for cross-sectoral collaboration, leading to policies that integrate environmental, social, and economic considerations. This shift is fostering an environment where adaptation initiatives can thrive.For instance, the incorporation of climate risk assessments into urban planning is becoming standard practice. Cities like Amsterdam are actively revising building codes and land-use regulations to integrate flood risk management into their infrastructure development.
This proactive approach enhances urban resilience against climate impacts.
Societal Changes Shaping Adaptation Strategies
Societal awareness and engagement are critical in shaping future adaptation efforts. As communities become more informed about climate risks, there is a growing demand for inclusive decision-making processes. Public participation is driving the localization of adaptation strategies, ensuring they reflect the unique needs of communities.An example can be seen in the participatory adaptation planning initiatives in the Philippines, where local communities are actively involved in identifying risks and developing tailored strategies.
This grassroots approach empowers communities and fosters a sense of ownership over adaptation measures.
Forecasting the Evolution of Adaptation Strategies
Looking ahead, adaptation strategies are expected to become more dynamic and technology-driven. The rise of smart technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) will enable real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making. These technologies will facilitate adaptive management practices that respond swiftly to changing conditions.Moreover, climate finance mechanisms are anticipated to evolve, providing more robust funding for adaptation initiatives.
The Green Climate Fund and similar entities are likely to expand their scope, focusing on innovative financing solutions that promote resilience-building efforts, especially in developing countries.In conclusion, the future of climate change adaptation is characterized by a blend of scientific innovation, policy evolution, and community engagement. As we embrace these trends, the potential to build resilient systems that can withstand the impacts of climate change becomes increasingly attainable.
Concluding Remarks
In summary, Climate Change Adaptation Strategies play a pivotal role in building resilience against the adverse effects of climate change. By integrating policy frameworks, community engagement, and technological innovations, we can enhance our adaptive capacity and ensure a sustainable future. As we look ahead, continuous learning and adaptation will be key to navigating the complex landscape of climate challenges.
Question & Answer Hub
What is climate change adaptation?
Climate change adaptation refers to the process of adjusting practices, processes, and structures to minimize damage from climate change effects.
Why are adaptation strategies important?
Adaptation strategies are vital for reducing vulnerability and increasing resilience to climate impacts, ensuring the sustainability of communities and economies.
How is community involvement incorporated in adaptation?
Community involvement is essential as local knowledge and participation lead to more relevant and effective adaptation strategies tailored to specific challenges.
What role does technology play in adaptation?
Technology enhances adaptation efforts through innovations like early warning systems and climate-resilient crops, though it also poses risks if over-relied upon.
How are adaptation strategies monitored?
Adaptation strategies are monitored through various methods and indicators that evaluate their effectiveness and inform necessary adjustments over time.